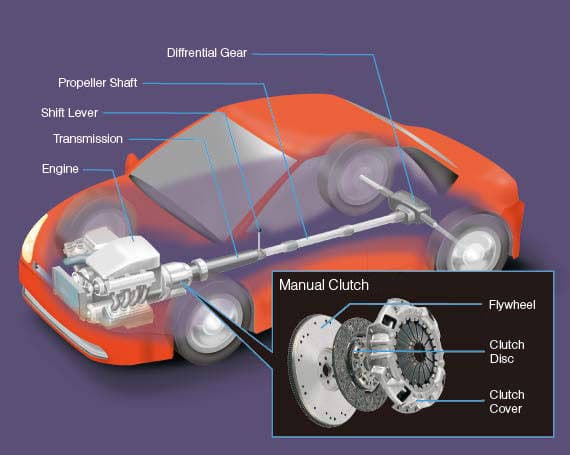
You're definitely familiar with the clutch if you've ever driven a car with a manual transmission. It is necessary to push the third pedal in order to change gears.
You're definitely familiar with the clutch if you've ever driven a car with a manual transmission. It is necessary to push the third pedal in order to change gears. However, if you've only driven automobiles with automatic transmissions, you might not understand what the clutch performs. What exactly is a clutch, and why would you require one? Because your engine is always turning, the wheels must be able to disengage so that they can stop moving. The clutch comes into play at this point. It has the ability to release the wheels without shutting down the engine.
What is the Purpose of the Clutch?
Although everyone is aware that a car is powered by an engine, not everyone is familiar with a clutch or how it operates. Your power transmission from the driving shaft to the driven shaft is engaged and disengaged by this device. It links rotating shafts and can have two or more under your hood. The clutch is attached to both the engine shaft and the shafts that turn the wheels if you drive a manual transmission. While the motor will spin incessantly, you do not want the wheels to spin incessantly.
One of the spinning shafts, the driving member, will be connected to the engine or power unit, while the other revolving shaft, the driven member, will give work output. A drill, for example, has two shafts, one driven by a motor and the other by a drill chuck. According to HowStuffWorks, the clutch connects the shafts such that they can be engaged (spinning at the same speed), slipping (spinning at various speeds), or disengaged (spinning at different speeds) (spinning at different speeds). Typically, these motions are rotary; however, linear clutches are also feasible.
What are the clutch design considerations?
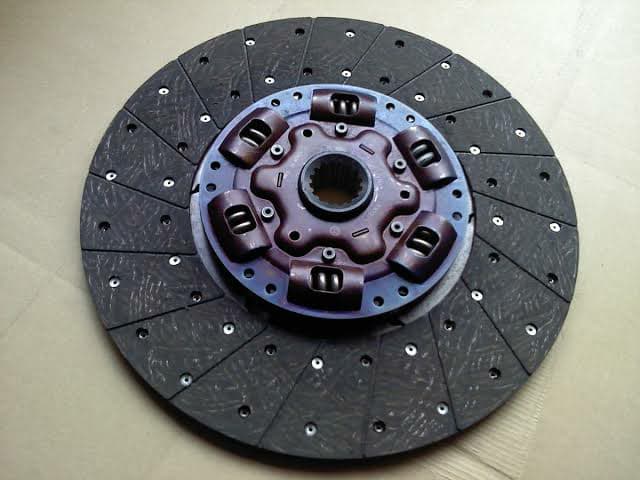
The connection between the wheels and the motor must be cut in order for your car to come to a stop without the complete engine shutting down. Your clutch consists of two primary components:
- A clutch plate is a device that allows you to change gear
- The flywheel is a device used to propel a vehicle
Spring tension is maintained on a plate that pushes up against the clutch plate. The clutch plate is also pushed up against the flywheel by these springs. According to AAMCO, the engine shaft is connected to the wheel shafts, causing both to turn at the same time. You must engage the clutch in order for the opposite to occur.
This pulls the pressure plate away from the clutch plate, effectively breaking the link between the rotating engine and the moving wheels. Although the wheels continue to spin, Autobutler indicates that this is due to their own momentum rather than the engine's power.
When driving a car with an automatic transmission, the clutch operates in a unique way. A torque converter is a component of a larger system that connects the engine to the transmission and drives the wheels. In fact, clutches come in a variety of shapes and sizes, including:
- Friction clutches are the result of friction.
- Plate clutches with many plates
- Clutches of cones
- Centrifugal clutches are a type of centrifugal clutch.
- Systems that are wet vs. systems that are dry
Clutches rely on frictional forces to function. Frictional clutches connect one moving element to another that is moving at a different pace, or not at all, in order to keep them moving at the same speed and avoid slippage. Friction is created using a variety of materials. They are as follows:
- Organic compound resin
- Ceramic Composite Paper with Copper Wire
Many plate clutches contain multiple driving members, making them excellent for racing automobiles like Formula 1, the Indianapolis 500, and club racing. The clutch in drag racing automobiles is subjected to a great deal of damage, which is why this sort of clutch is so common. Motorcycles and diesel engines with mechanical transmissions also use it. You might also find one in a car with an electronically controlled all-wheel-drive system, as well as in some transfer cases.
Cone clutches have a conical shape, and their taper means they approach and retreat more slowly than disc clutches. This means that the shift hub and gear wheel speeds are coordinated to provide smoother shifting while changing gears.
A centrifugal clutch is most commonly found in vehicles such as mopeds or machines such as chainsaws, where the engine speed determines the clutch's state. When the engine's rpms rise above or fall below a specified threshold, centrifugal force is used to engage or disengage the clutch.
A wet clutch differs from a dry clutch in that it is lubricated and is immersed in a cooling solution to maintain it clean and extend its life. It's worth noting, though, that this style of clutch will lose energy due to its slickness. Multiple clutch discs stacked on top of each other can help to compensate for this slippage. A dry clutch, on the other hand, relies on friction to operate.
Typical Clutch Issues
It is possible to get up to 80,000 miles out of your clutch, according to AAMCO, but you must treat it properly. The following are some of the most prevalent clutch issues:
- Wear: The materials in your clutch will wear out over time due to constant friction.
- The tension required to push and pull the cable is insufficient.
- Leaks: If the fluids in the cylinders leak out, there will be insufficient pressure for the clutch to work correctly.
- When you press the clutch or gas pedal, the improper amount of force is communicated.
- If air gets into the line where fluid should be, there won't be enough pressure in the system for it to work properly.
- a tight clutch: If you have to exert a lot of force to get your clutch to engage, this could signal a problem.
Knowing what a clutch is and how it works will help you see when your car isn't working properly. Change gears rapidly and avoid riding the clutch, among other things, to avoid issues.
Having issues with your clutch? The Most Common Problems Are Listed Below.
When the clutch is let out, car owners with manual gearboxes may feel a similar phenomenon — an unusual vibration. What is the reason for this? We'll go through what could go wrong with your car's clutch and how to spot the problem right away.
1. A leak in the master or slave cylinder is possible. There are two types of clutches: hydraulic and cable-operated. Hydraulic clutches, which rely on fluid from the cylinders to actuate the clutch, are now standard in most cars. It may become impossible to provide hydraulic pressure if the master or slave cylinders begin to lose fluid.
If your cylinders are leaking, you'll see fluid accumulating under your car. Alternatively, fluid spilling on the exhaust pipe may generate a peculiar odor.
2. The throwout may need to be replaced. The pressure plate is actuated by the throwout bearing. It rides on the transmission's input shaft. It can become worn out and lose lubrication as a result of its frequent spinning.
If you hear a squeaking sound when the car is running but the sound stops when the clutch is engaged, the problem could be a damaged bearing.
3. It's possible that the clutch disc is worn out. The clutch disc is splined to the transmission shaft. Due to risky driving practices, the disc will most certainly wear out over time.
How to spot the problem: When the clutch disc wears out, the clutch pedal releases more forcefully. In this case, a car's acceleration under a big load may be challenging.
4. It's possible that the flywheel will become warped. Similar to how rotors are joined to axles, the flywheel is bolted to the end of the crankshaft. The flywheel might overheat over time, causing it to deform.
How to find out whether there's a problem: You may feel vibrations as you let out the clutch as the flywheel's surface gets uneven.
5. It's possible that your pressure plate is worn out. The clutch disc is clamped to the flywheel by the pressure plate. Because it is one of the most often used elements of your clutch, it is prone to wear.
How to find out whether there's a problem: A damaged pressure plate, like a damaged flywheel, can cause vibration when the clutch is released.
Identifying the cause of your clutch
If you think there's a problem with your clutch, there's a simple test you can do to see if that's the problem. You can be fairly certain that the clutch is not the problem if you follow the next four steps without hearing any weird noises.
1. Turn the key in the ignition, make sure the handbrake is engaged, and shift the vehicle into neutral.
2. Listen for a noise that sounds like a low growl when the engine is turned on but the accelerator or clutch pedal is not depressed. Continue to the next step if you don't hear anything. If you hear a growling sounds, you most likely have an issue with your clutch's transmission. If you are unable to repair the problem yourself, you should take your vehicle to a mechanic and inform them of the noise as soon as possible.
3. Don't put the car in drive; instead, partially depress the clutch pedal and listen for any noises. Continue to the next step if you don't hear anything. If you hear a high-pitched squeaking sound when you press the clutch pedal, you have a clutch problem. Problems with the clutch release or throw-out bearings are frequently the cause of this type of noise.
4. Completely depress the clutch pedal. Listen for any unexpected sounds coming from the vehicle once more. If it starts to screech, you most likely have a problem with the pilot bearing or bushing.
If you don't hear any noises throughout any of these tests, it's unlikely that you have a clutch problem. If you're concerned about your car's performance, take it to a garage and get it looked at by a specialist to figure out what's wrong. If you notice the clutch slipping, sticking, or gripping while driving, it's possible that the entire clutch has worn out and you'll need to replace it.
If you hear any of the noises indicated above, make a note of what type of noise you hear and when it occurs. This may allow you to merely repair the damaged part of the clutch, which will be far less expensive than replacing the entire clutch.